Delving into Truman’s Scientific Guide to Pest Management, this comprehensive guide immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative that unravels the complexities of pest management. With a focus on integrated pest management (IPM) principles, this guide provides a holistic approach to managing pests effectively, minimizing their impact on various industries and ensuring the well-being of individuals and the environment.
Truman’s Scientific Guide to Pest Management offers a comprehensive understanding of pest biology, identification, monitoring, and control methods. It explores the advantages and disadvantages of chemical and non-chemical pest control techniques, emphasizing the importance of combining multiple strategies for effective pest management.
Case studies and success stories further illustrate the practical application of IPM principles, showcasing the benefits and outcomes of successful pest management programs.
Introduction to Truman’s Scientific Guide to Pest Management

Truman’s Scientific Guide to Pest Management provides comprehensive and authoritative guidance on managing pests effectively in various industries. Pest management is crucial for protecting public health, ensuring food safety, minimizing crop losses, and maintaining the integrity of structures and materials.
Principles of Pest Management
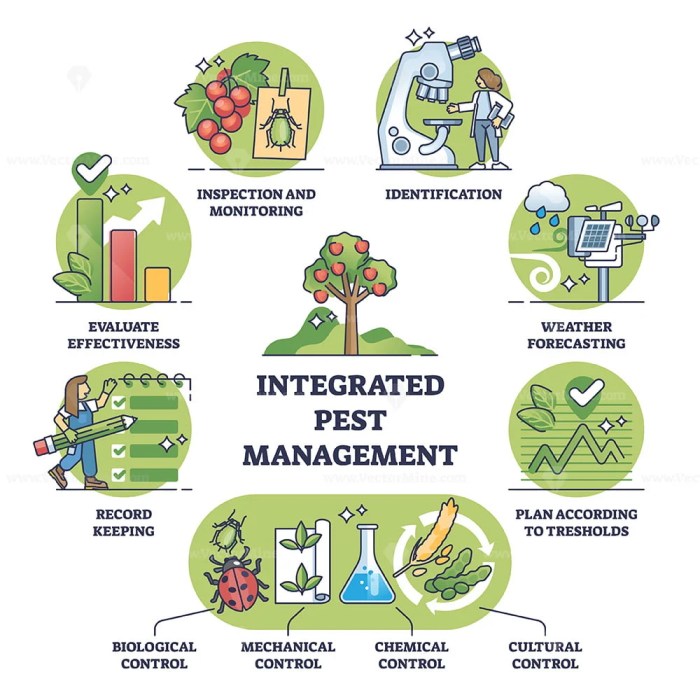
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM is a holistic approach that combines multiple pest control methods to manage pests effectively while minimizing environmental impact. It emphasizes monitoring, identification, and threshold levels to determine the appropriate control measures.
Monitoring, Identification, and Threshold Levels
Regular monitoring helps detect pest infestations early on. Accurate identification of pests is essential for selecting effective control methods. Threshold levels determine the point at which pest populations require intervention.
Pest Control Methods, Truman’s scientific guide to pest management
Pest control methods include:
- Biological control:Using natural enemies to suppress pests
- Chemical control:Applying pesticides to kill or repel pests
- Cultural control:Modifying the environment to make it less favorable for pests
Common Pests and Their Management
| Pest Name | Description | Habitat | Control Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rodents | Small mammals that can transmit diseases and damage property | Urban and rural areas | Trapping, baiting, exclusion |
| Cockroaches | Insects that can contaminate food and spread allergens | Warm, moist areas | Baits, traps, chemical treatments |
| Termites | Wood-destroying insects that can cause significant structural damage | Wood structures | Chemical treatments, baiting, exclusion |
| Stored product pests | Insects and rodents that infest stored food products | Food storage facilities | Sanitation, traps, chemical treatments |
| Mosquitoes | Insects that can transmit diseases and cause discomfort | Standing water | Larviciding, adulticiding, mosquito nets |
Chemical Pest Control: Truman’s Scientific Guide To Pest Management

Types of Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides include:
- Insecticides
- Herbicides
- Fungicides
- Rodenticides
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chemical Pesticides
Advantages:
- Rapid and effective pest control
- Widely available and affordable
Disadvantages:
- Potential for environmental harm
- Development of pest resistance
- Non-selective, can harm beneficial organisms
Guidelines for Safe and Effective Use of Pesticides
- Follow label instructions carefully
- Use only approved pesticides
- Wear appropriate protective gear
- Dispose of pesticides properly
Q&A
What is the significance of pest management?
Pest management plays a crucial role in various industries, including agriculture, food processing, healthcare, and residential settings. It protects crops, ensures food safety, prevents the spread of diseases, and safeguards human health and well-being.
What are the key principles of integrated pest management (IPM)?
IPM involves a holistic approach that combines multiple pest control methods, including biological, cultural, and chemical techniques. It emphasizes monitoring pest populations, identifying thresholds, and implementing targeted control measures to minimize pest damage while preserving beneficial organisms and the environment.
What are the advantages of using non-chemical pest control methods?
Non-chemical pest control methods, such as physical barriers, traps, and biological control, offer several advantages. They are often safer for humans and the environment, can reduce the risk of pesticide resistance, and can be more sustainable in the long term.