In the realm of digital security, John receives an encrypted document using asymmetric cryptography from Alex, a captivating tale that unfolds the intricacies of this enigmatic field. Asymmetric cryptography, a cornerstone of modern encryption, empowers users to safeguard sensitive information with remarkable efficiency.
This narrative delves into the concepts, applications, and considerations surrounding this transformative technology, offering a comprehensive exploration for the curious and discerning reader.
Asymmetric cryptography stands as a testament to human ingenuity, providing a secure and reliable means of transmitting confidential data across vast digital landscapes. This introductory paragraph sets the stage for an engaging journey into the world of cryptography, where John’s encounter with an encrypted document serves as a compelling catalyst for unraveling the mysteries that lie ahead.
Asymmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography is a type of cryptography that uses two different keys, a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt messages, while the private key is used to decrypt them. This makes it impossible for anyone other than the intended recipient to read the message.Asymmetric
cryptography is based on the mathematical concept of one-way functions. A one-way function is a function that is easy to compute in one direction, but very difficult to compute in the opposite direction. For example, it is easy to multiply two large prime numbers together, but it is very difficult to factor the resulting number.Asymmetric
cryptography uses two different one-way functions. The first function is used to generate the public and private keys. The second function is used to encrypt and decrypt messages.The most common asymmetric encryption algorithm is the RSA algorithm. The RSA algorithm was developed by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in 1978. The RSA algorithm is based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
Encrypted Document
An encrypted document is a document that has been encrypted using a cryptographic algorithm. Encryption is the process of converting plaintext into ciphertext. Ciphertext is a form of data that cannot be read or understood without the proper decryption key.The
purpose of encrypting a document is to protect its contents from unauthorized access. Encryption can be used to protect sensitive information, such as financial data, medical records, and trade secrets.To encrypt a document using asymmetric cryptography, the sender first generates a public and private key pair.
The sender then uses the public key to encrypt the document. The encrypted document can then be sent to the recipient.The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the document. The private key is the only key that can decrypt the document.
Sender and Receiver
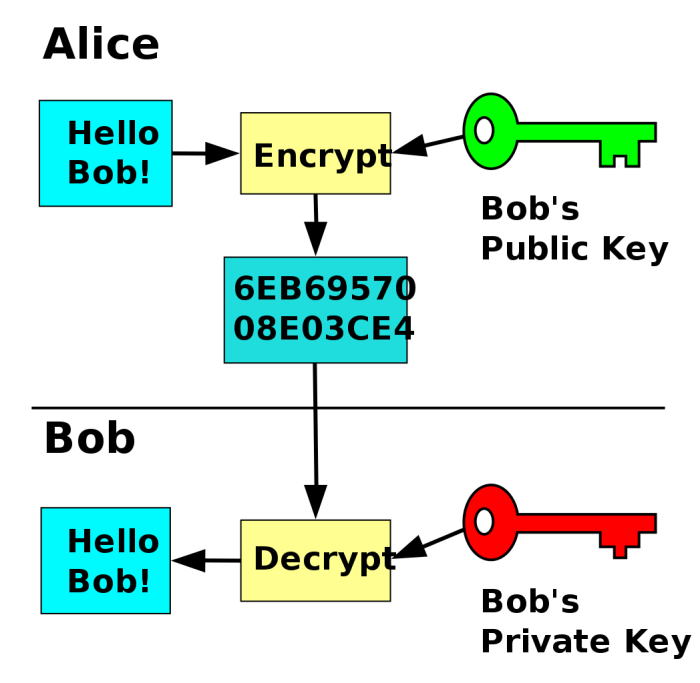
In asymmetric cryptography, the sender is the person who encrypts the message, and the receiver is the person who decrypts the message.The sender generates a public and private key pair. The public key is used to encrypt the message, and the private key is used to decrypt the message.The
sender sends the encrypted message to the receiver. The receiver uses their private key to decrypt the message.Secure key exchange is essential for asymmetric cryptography. If the public key is compromised, then anyone can encrypt messages that the receiver will be able to decrypt.
Key Management: John Receives An Encrypted Document Using Asymmetric Cryptography From Alex
Key management is the process of generating, storing, and protecting cryptographic keys. Proper key management is essential for the security of asymmetric cryptography.There are a number of different methods for storing and protecting keys. One common method is to use a hardware security module (HSM).
An HSM is a tamper-resistant device that is used to store and protect cryptographic keys.Another method for storing and protecting keys is to use a key management system (KMS). A KMS is a software system that is used to manage cryptographic keys.
A KMS can be used to generate, store, and protect keys.It is important to have a plan for key recovery in case a key is lost or compromised. Key recovery is the process of recovering a cryptographic key from a backup.
Security Considerations
There are a number of potential security risks associated with asymmetric cryptography. One risk is that the public key could be compromised. If the public key is compromised, then anyone can encrypt messages that the receiver will be able to decrypt.Another
risk is that the private key could be compromised. If the private key is compromised, then anyone can decrypt messages that the sender has encrypted.It is important to use strong encryption algorithms and key lengths to mitigate the risks associated with asymmetric cryptography.
Strong encryption algorithms are difficult to break, and long key lengths make it more difficult to guess the key.It is also important to have a plan for key recovery in case a key is lost or compromised.
Applications

Asymmetric cryptography is used in a wide variety of applications, including:* Secure communication: Asymmetric cryptography can be used to secure communication between two parties. For example, asymmetric cryptography can be used to encrypt email messages and instant messages.
Digital signatures
Asymmetric cryptography can be used to create digital signatures. A digital signature is a mathematical proof that a message was sent by a particular person.
Authentication
Asymmetric cryptography can be used to authenticate users. For example, asymmetric cryptography can be used to authenticate users to a website or to a network.
Key exchange
Asymmetric cryptography can be used to exchange keys securely. For example, asymmetric cryptography can be used to exchange keys between two parties who want to communicate securely.
Helpful Answers
What is the key difference between public and private keys in asymmetric cryptography?
In asymmetric cryptography, public keys are used to encrypt messages, while private keys are used to decrypt them. The public key is shared with others, while the private key is kept secret.
How does asymmetric cryptography ensure secure key exchange?
Asymmetric cryptography utilizes a unique mathematical relationship between public and private keys. Even if the public key is compromised, the private key remains secure, ensuring the confidentiality of encrypted messages.
What are some real-world applications of asymmetric cryptography?
Asymmetric cryptography finds widespread application in various domains, including secure communication, digital signatures, and blockchain technology.