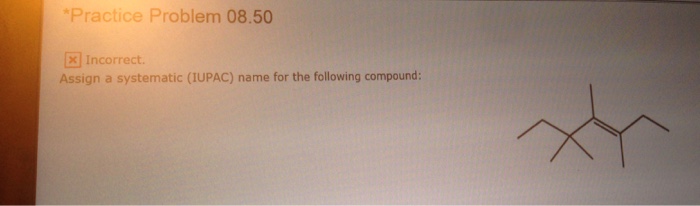
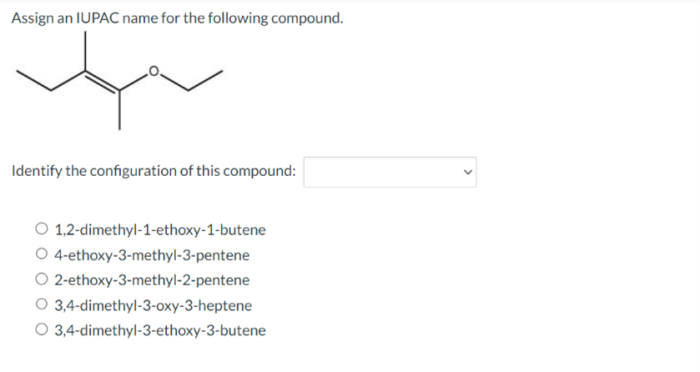
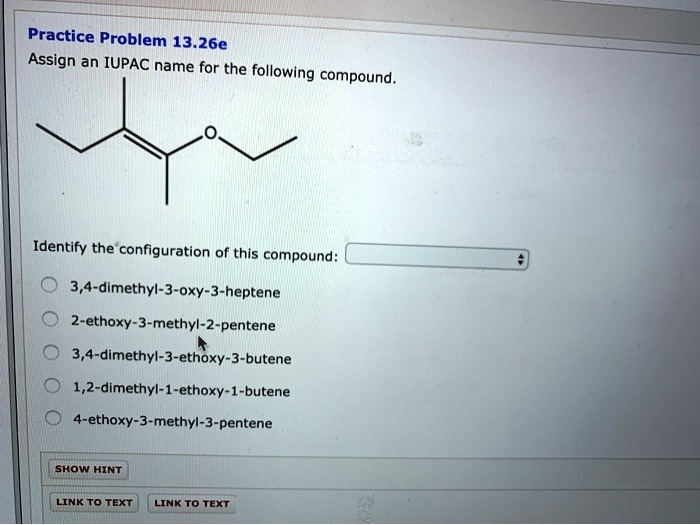
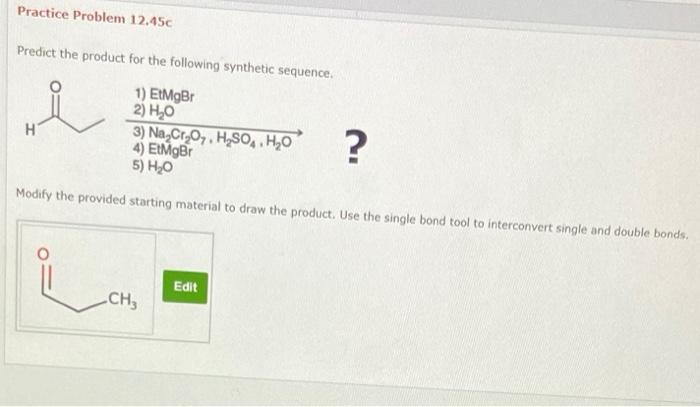
Assign an IUPAC name for the following compound: a journey into the fascinating world of organic chemistry, where we unravel the secrets of naming organic compounds according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) guidelines. This comprehensive guide empowers you with the knowledge and skills to systematically identify and name organic compounds, enabling effective communication and understanding within the scientific community.
Delving into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, we embark on an exploration of functional groups, parent chains, substituents, and numbering, equipping you with the tools to decipher the structural complexities of organic molecules. By mastering the art of IUPAC naming, you gain the ability to convey the precise molecular structure of compounds in a standardized and universally accepted language, facilitating seamless collaboration and knowledge exchange.
IUPAC Nomenclature: Assign An Iupac Name For The Following Compound
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method of naming organic compounds. It was developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is used by chemists around the world. IUPAC nomenclature is based on a set of rules that ensure that each compound has a unique name that reflects its structure.
The rules of IUPAC nomenclature are complex, but they can be summarized as follows:
- The name of a compound is based on its parent chain.
- The parent chain is the longest chain of carbon atoms in the compound.
- The name of the parent chain is based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain.
- Substituents are groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain.
- Substituents are named according to their structure.
- The name of a compound is written by combining the name of the parent chain with the names of the substituents.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have characteristic chemical properties. Functional groups are used to classify organic compounds and to predict their reactivity.
The most common functional groups include:
- Alkanes
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
- Alcohols
- Ethers
- Aldehydes
- Ketones
- Carboxylic acids
- Esters
- Amides
Parent Chain
The parent chain is the longest chain of carbon atoms in a compound. The name of the parent chain is based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain.
The following table shows the names of the parent chains for compounds with 1 to 10 carbon atoms:
| Number of Carbon Atoms | Name of Parent Chain |
|---|---|
| 1 | Meth |
| 2 | Eth |
| 3 | Prop |
| 4 | But |
| 5 | Pent |
| 6 | Hex |
| 7 | Hept |
| 8 | Oct |
| 9 | Non |
| 10 | Dec |
Substituents
Substituents are groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain. Substituents are named according to their structure.
The most common substituents include:
- Alkyl groups
- Alkenyl groups
- Alkynyl groups
- Halo groups
- Hydroxy groups
- Ether groups
- Aldehyde groups
- Ketone groups
- Carboxylic acid groups
- Ester groups
- Amide groups
Numbering the Parent Chain
The parent chain is numbered from one end to the other. The carbon atom at the end of the chain with the lowest number is assigned the number 1.
The following rules are used to number the parent chain:
- The carbon atom that is attached to the most substituents is assigned the lowest number.
- If two or more carbon atoms are attached to the same number of substituents, the carbon atom that is closest to the end of the chain is assigned the lowest number.
- If two or more carbon atoms are attached to the same number of substituents and are equidistant from the end of the chain, the carbon atom that is attached to the highest priority substituent is assigned the lowest number.
Putting it All Together, Assign an iupac name for the following compound
To assign an IUPAC name to a compound, you need to:
- Identify the parent chain.
- Identify the substituents.
- Number the parent chain.
- Name the substituents.
- Combine the name of the parent chain with the names of the substituents.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key principles of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature follows a set of rules and guidelines established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry to provide a systematic and standardized approach to naming organic compounds. These principles ensure consistency and clarity in the naming of compounds, regardless of their complexity or structural diversity.
How do I determine the parent chain of an organic compound?
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule. To identify the parent chain, start by identifying the functional groups present and then select the chain that contains the highest priority functional group. The priority of functional groups is determined by their seniority, which is assigned based on their chemical properties and bonding characteristics.
What is the significance of numbering the parent chain?
Numbering the parent chain is crucial for assigning IUPAC names correctly. The numbering starts from the end of the parent chain that gives the lowest numbers to the substituents. This systematic numbering ensures that the location of substituents along the chain is clearly indicated, avoiding ambiguity and facilitating the identification of the compound.