Embarking on a journey into the realm of genetics, we delve into the fascinating world of Part C monohybrid cross problems, where the principles of inheritance unravel before our eyes. These problems play a pivotal role in understanding the fundamental concepts of genetics and their applications in unraveling the mysteries of inheritance patterns.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of Part C monohybrid cross problems, empowering you with the knowledge to tackle these challenges with confidence. From defining the concept of “part C” to mastering strategies for solving these problems, we will uncover the significance of these problems in genetic research and their contributions to our understanding of inheritance.
Part C Monohybrid Cross Problems

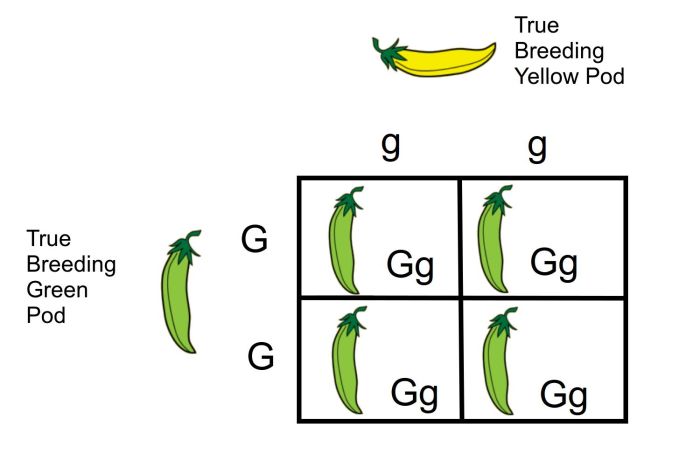
In the context of monohybrid crosses, “part C” refers to the third part of a typical problem, which typically involves predicting the phenotypic ratio of the offspring.
Part C problems are significant because they allow geneticists to determine the probability of specific phenotypes appearing in a population. By understanding the principles of part C problems, researchers can gain valuable insights into the inheritance patterns of traits and make predictions about future generations.
Strategies for Solving Part C Monohybrid Cross Problems
- Identify the dominant and recessive alleles:Determine which allele is dominant and which is recessive based on the information provided in the problem.
- Set up a Punnett square:Construct a Punnett square to represent the possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited by the offspring.
- Count the genotypes and phenotypes:Determine the number of offspring with each genotype and phenotype based on the Punnett square.
- Calculate the phenotypic ratio:Calculate the ratio of offspring with each phenotype, typically expressed as a fraction or percentage.
Applications of Part C Monohybrid Cross Problems
Part C monohybrid cross problems have numerous applications in genetic research, including:
- Predicting the inheritance of traits:Part C problems allow researchers to predict the probability of specific traits being inherited by offspring.
- Understanding genetic disorders:By analyzing part C problems, geneticists can gain insights into the inheritance patterns of genetic disorders and develop strategies for genetic counseling.
- Improving crop and livestock breeding:Part C problems are used in agriculture to optimize breeding programs and improve the genetic traits of crops and livestock.
Advanced Concepts in Part C Monohybrid Cross Problems
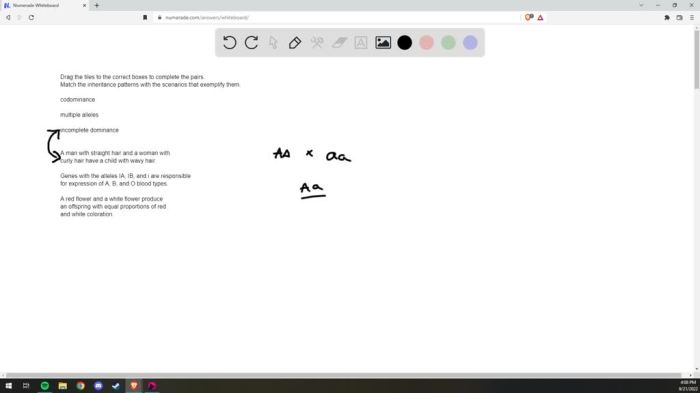
- Incomplete dominance:In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant, resulting in an intermediate phenotype in the offspring.
- Codominance:In codominance, both alleles are expressed in the offspring, resulting in a distinct phenotype that is different from either parent.
- Multiple alleles:Some genes have multiple alleles, which can lead to more complex inheritance patterns in part C problems.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study:A geneticist is studying the inheritance of flower color in pea plants. The dominant allele (P) produces purple flowers, while the recessive allele (p) produces white flowers. In a cross between a homozygous purple-flowered plant (PP) and a homozygous white-flowered plant (pp), what is the expected phenotypic ratio of the offspring?
Example:In a monohybrid cross between a homozygous tall pea plant (TT) and a homozygous short pea plant (tt), what is the expected phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation?
FAQs
What is the significance of “part C” in monohybrid cross problems?
Part C refers to the third part of a monohybrid cross problem, where students are tasked with determining the phenotypic ratio of the offspring. It is significant because it tests the understanding of inheritance patterns and the ability to apply Punnett square analysis.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills for Part C monohybrid cross problems?
Practice is key! Engage in solving numerous problems, analyze the patterns, and seek guidance from teachers or online resources. Understanding the concepts of dominance, recessiveness, and allele combinations is crucial.
What are some real-world applications of Part C monohybrid cross problems?
These problems have applications in agriculture, medicine, and evolutionary biology. They help us predict inheritance patterns in plant and animal breeding, understand genetic disorders, and trace the evolution of species.